How to Give an IM Injection
© 2008-12 Kathy Quan RN BSN All Rights Reserved
The injection site will be determined by the volume of medication to be injected. Other considerations are the age of the patient, the size and weight of the patient
and mobility issues. The patient’s ability to relax and cooperate can also play a role in determining a safe injection site. Needle size depends on factors such as the site, medication and size/weight of the patient.
Land marking of the IM site is essential to avoid nerves such as the sciatic nerve. For this reason, the dorsal gluteal site is often avoided because improper land marking can lead to damage of the sciatic nerve. With proper land marking it can be an effective site with less discomfort than other sites.
Choices for IM injection sites are the deltoid, dorsal gluteal, ventrogluteal, and vastus lateralis. In children under 2 years, it is recommended to always use the vastus lateralis (antero- lateral thigh.)
Difficulty: Average
Time Required: about 5 minutes
Here’s How:
- Confirm the medication order.
- Check the dispensed medication with the order.
- Gather supplies, wash your hands and prepare the syringe.
- Identify the patient. Explain the injection order and procedure to the patient.
- Wash your hands.
- Continue to explain the procedure to the
patient step-by-step as you choose an appropriate site and prep the patient for privacy. Palpate the site to ensure the muscle can withstand the volume of medication to be injected. - Prepare your supplies. Open swabs and a Band-Aid.
NEXT:
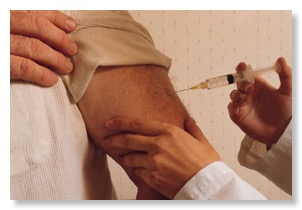
- Don gloves.
- Swab the injection site with an alcohol pad. Swab in a circular motion outward from the intended site 5 cm. Allow the alcohol to dry.
- Spread the tissue taut with your non-dominant hand. Have the patient relax and take a deep breath, as he inhales, insert the needle at a 90 degree angle in a quick dart-like motion.
- Hold the syringe barrel with your non-dominant hand and draw upwards on the plunger. If you aspirate blood, withdraw the needle and prepare a new syringe.
- If no blood returns, inject the medication at a
slow steady rate to minimize discomfort. - When all of the medication has been injected, quickly withdraw the needle and apply pressure to the injection site with a fresh alcohol pad. This helps prevent medication from seeping back into subcutaneous tissue. Some medications may recommend massaging the injection site for 1-2 minutes, but for some this may be contraindicated.
- Apply Band-Aid if needed.
Doff gloves and wash your hands.
Assess patient for response to the injection.
Document:
time, medication, dose, route, site and patient’s response to injection.
Notify the practitioner immediately of any untoward response or reaction.
Tips:
For dorsal gluteal site have the patient lie prone with toes pointing in.
For ventrogluteal site have the patient lie on one side with the upper leg flexed and forward
For vastus lateralis site have the patient lie supine with toes pointing midline.
For deltoid site have the patient sitting with elbow bent and forearm supported.
If you are self injecting, be sure that a nurse or physician has instructed and observed your technique before injecting yourself alone.
Supplies needed:
Medication order and medication Syringe, needle, alcohol swabs, Band-Aid Gloves
photos from Microsoft.com